In the realm of business continuity, disaster recovery planning stands as a crucial linchpin. It’s the bedrock upon which an organization’s ability to rebound from data losses or IT disruptions due to either natural catastrophes or human-made incidents rests. The fundamental objective of a well-constructed disaster recovery plan (DRP) is to facilitate a swift recovery process with minimal operational disruptions. In this article, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of disaster recovery planning and guide you through the indispensable steps necessary to craft and implement an effective DRP template.
Understanding the Essence of Disaster Recovery Plans (DRPs)
A disaster recovery plan (DRP) is more than a mere procedural document; it’s a strategic playbook meticulously crafted to empower organizations to rise from the ashes of unforeseen events that could potentially throw a wrench into their technology systems and overall business operations. It holds a significant place within the realm of security and business continuity planning.
The recent history of our world is a testament to the capricious nature of life. Events such as the global COVID-19 pandemic and the devastating wildfires of 2021 have underscored the paramount importance of being prepared for calamities. Businesses must ensure the unswerving delivery of their services even in the most adverse circumstances. This is where the disaster recovery plan takes the spotlight. This plan involves:
- Identification of critical resources pivotal for the smooth functioning of operations.
- Formulation of strategies to protect and securely back up these indispensable resources.
- Mitigation of the negative impact of disasters and swift restoration of operations.
- Furnishing a meticulously sequenced set of steps to be executed during a crisis.
- Clearly defining roles, responsibilities, resources, and necessary technologies for recovery.
- Tailoring recovery strategies to suit various types of disasters.
- Establishing a culture of regular plan reviews and updates to enhance its efficacy.
In a nutshell, a well-structured disaster recovery plan functions as a roadmap that adeptly guides businesses through turbulent times, steering them towards normalcy restoration, and ensuring an uninterrupted flow of services.
The Indispensable Role of a Stable DRP
A stable Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) is the cornerstone for an organization’s successful recovery from disruptive incidents. Devoid of a robust plan, the arduous task of managing and rebounding from diverse disasters becomes a formidable challenge. These potential disruptions encompass a gamut ranging from critical IT outages and malicious cyberattacks to the unforgiving wrath of natural forces and even man-made adversities.
The Implications of Disruptions:
Disruptions, beyond their visible impact, carry substantial financial costs. According to a 2022 snapshot by Dell on the Global Data Protection Index (GDPI), cyberattacks and unforeseen disruptions have been surging. A staggering 86% of organizations have faced unplanned interruptions within the past year alone, leading to an estimated aggregate cost of over $900,000. The gravity of this figure is substantially higher than previous year’s by 33%.
However, the repercussions of disruptions extend beyond financial realms. Business continuity is inherently tied to reputation and the foundation of trust that an organization builds with its stakeholders. When businesses can respond effectively to disruptions, they manifest their unwavering commitment to the seamless provision of services while safeguarding sensitive data.
Crafting an Effective Disaster Recovery Plan: The Essential Steps
Step 1: Formation of an Expert Cohort
The preliminary phase involves the assembly of a team composed of seasoned experts and key stakeholders. This multifaceted team includes department heads, HR representatives, PR officers, infrastructure experts, and senior management. In addition, external stakeholders like property managers and emergency responders should be woven into this fabric of preparedness.
Step 2: Scrutiny Through Business Impact Assessment
The foundation of a robust disaster recovery plan is a meticulous evaluation of the potential impacts of disruptive incidents. This is undertaken through a thorough Business Impact Analysis (BIA). This examination dissects the organization into its core components: assets, services, and functions. Each element is painstakingly evaluated to ascertain the plausible consequences of its failure. Considerations span from financial losses and damage to reputation to potential regulatory penalties. This evaluation unearths the window of time the organization has before the negative impacts set in following the failure of a particular asset or function.
Step 3: Metric Determination for the DRP
After the Business Impact Analysis (BIA), it becomes pivotal to crystallize the organization’s IT infrastructure and processes into quantifiable metrics. These metrics, in the form of Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs), provide the compass for recovery goals in the aftermath of a disruption.
Step 4: Delving into Comprehensive Risk Assessment
An all-encompassing risk assessment forms the bedrock of a well-rounded disaster recovery plan. This stage involves the meticulous analysis of potential threats that could potentially derail the organization’s smooth functioning. This entails identifying risks ranging from natural disasters, national emergencies, regional crises, and regulatory shifts to application failures, data center debacles, communication breakdowns, and the ominous specter of cyberattacks. Each risk identified then demands its own tailored strategies for mitigation and management, encompassing elements such as hardware maintenance, protection against power outages, and robust security measures to fend off cyberattacks.
Step 5: Selecting the Ideal DRP Type
When it comes to disaster recovery planning, a one-size-fits-all approach falls short. The decision on the appropriate disaster recovery plan type hinges on the outcomes of previous steps and factors in the organization’s DRP budget. Several avenues beckon, including the option of Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), cloud-based DRP, virtualization-based DRP, and the datacenter DRP. The selection should be a judicious one, grounded in alignment with the organization’s specific requirements and available resources.
Step 6: Crafting a Precise Disaster Recovery Runsheet
This step entails the creation of a comprehensive runsheet, akin to a detailed manual, encapsulating every conceivable facet of the disaster recovery plan. This extends from minute details like Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs), Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs), and contact information for essential personnel to the delineation of roles, responsibilities, and precise recovery steps for each service. This runsheet, in essence, is a repository of the organization’s readiness for a calamity, replete with information packs for key personnel, passwords, access rights, configuration details gleaned from the inventory analysis, and even the appointment of a focal point of contact to navigate the aftermath of a disaster.
Example: Runsheet
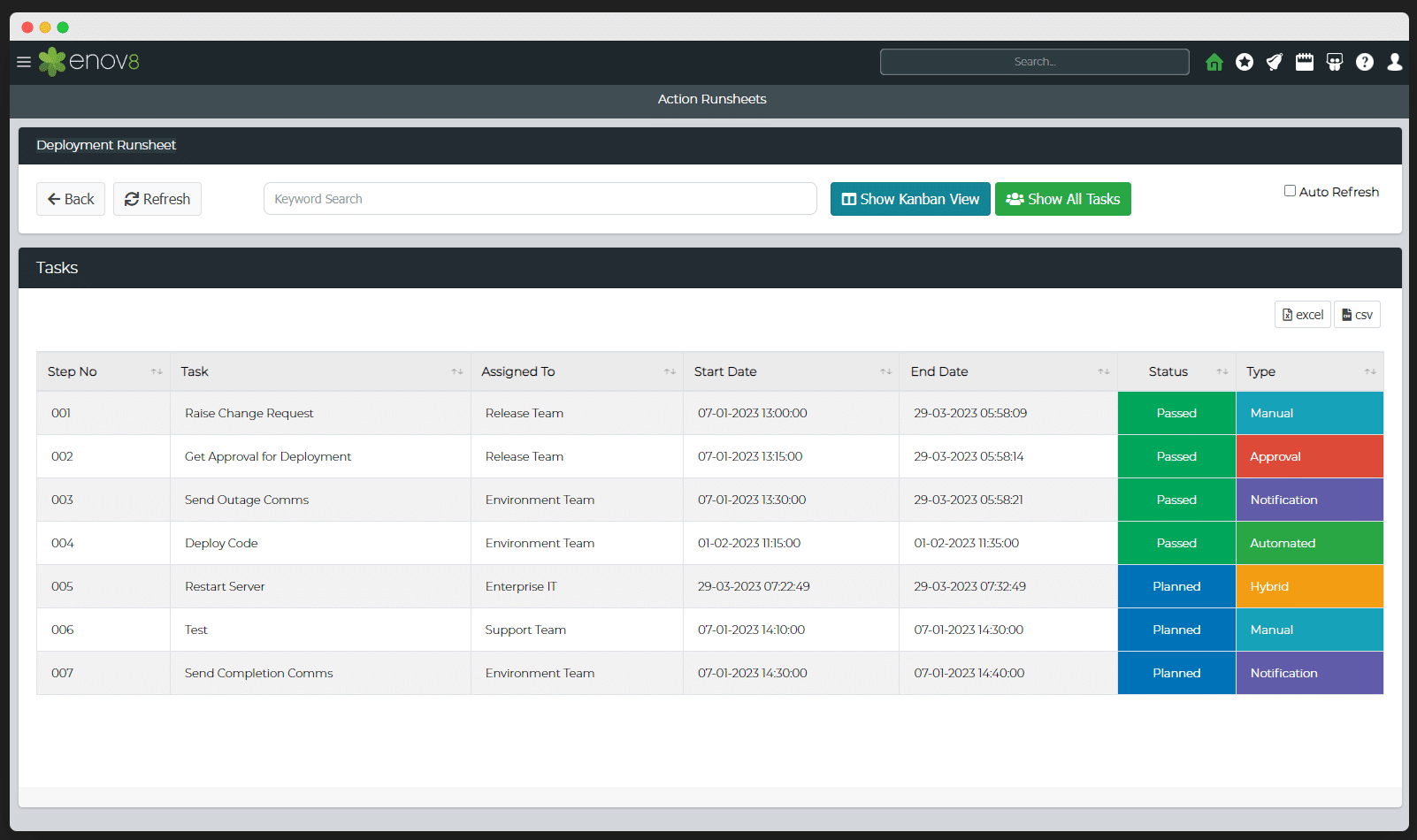
Step 7: Rigorous Testing and Validation
Testing forms the crucible where the disaster recovery plan’s true mettle is assessed. Rigorous testing is the crucible wherein the disaster recovery plan’s efficacy is subjected to the litmus test. Various testing methodologies exist, including simulations, complete interruption scenarios, walkthroughs, and parallel testing. Regular testing acts as a sentinel guarding against vulnerabilities and illuminates avenues for refinement.
Step 8: Establishing a Robust Communication Blueprint
The best-laid disaster recovery plan can falter in the absence of coherent communication strategies. Establishing effective channels of communication and clear-cut plans for disseminating information during the tumult of a disaster is indispensable. This encompasses employee training, scenario rehearsals, definition of roles, and the establishment of dedicated communication channels. Additionally, the PR team assumes the mantle of ensuring external stakeholders are well-informed and reassured, while the disaster recovery plan itself offers a reservoir of accurate insights about the crisis’s cause and expected recovery timelines. By nurturing a culture of well-structured communication, organizations fortify their capacity to navigate through crises and emerge with minimal disruption.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic landscape of business operations, the significance of disaster recovery planning cannot be overstated. It serves as the guardian of organizational resilience, enabling enterprises to weather the storm of unexpected disruptions with finesse and fortitude. This comprehensive guide has unveiled the core principles and intricate steps that form the bedrock of effective disaster recovery planning.
From understanding the essence of disaster recovery plans to assembling an expert team, scrutinizing business impact, and defining recovery metrics – each phase contributes to a holistic strategy that safeguards an organization’s integrity. The insight into crafting a precise playbook, rigorous testing, and establishing robust communication channels completes the tapestry of preparedness, ensuring a well-rounded response to crises.
In a world where the unforeseen can morph into the inevitable, disaster recovery planning is not just a theoretical exercise, but a strategic imperative. It is the lifeline that enables organizations to navigate through turbulent waters, minimize disruptions, and uphold their commitment to stakeholders. By navigating the eight essential steps outlined here, organizations can emerge as masters of disaster recovery, poised to confront challenges head-on, steer the ship of business continuity, and ensure an uninterrupted flow of services in even the most trying times.


