I. Introduction
In today’s digital age, software development and IT operations have become crucial components of many organizations’ business processes. However, as systems become more complex and interconnected, identifying and resolving issues and problems can be a time-consuming and challenging task. Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) is a critical metric that measures the average time it takes to detect an issue or problem in the system. Reducing MTTD can have a significant impact on system performance, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we will explore the concept of MTTD in more detail, discuss the factors that influence it, and provide some effective strategies for reducing MTTD and improving system efficiency.
II. What is Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)?
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) is a metric used to measure the average time it takes to identify an issue or problem in a system. MTTD is a critical metric because it directly impacts the Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), which is the average time it takes to fix an issue or problem in the system. The longer it takes to detect an issue, the longer it will take to fix it, leading to increased downtime, customer dissatisfaction, and potential revenue loss.
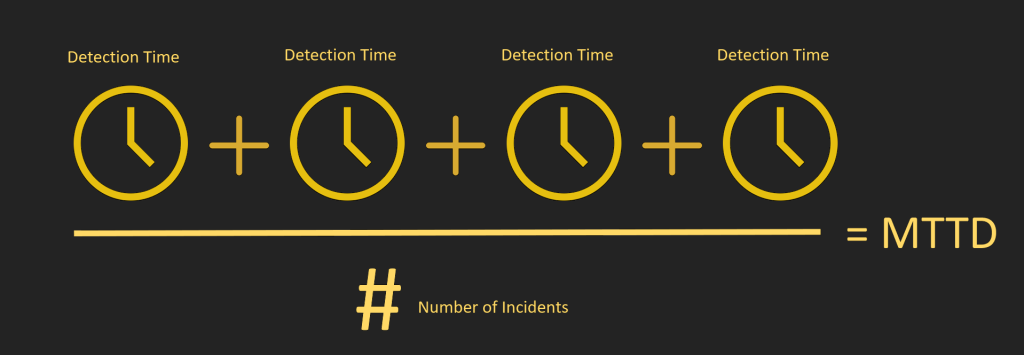
MTTD can be influenced by various factors, such as the complexity of the system, the quality of monitoring tools, and the effectiveness of communication and collaboration among teams. Systems with high complexity and interdependence may require more time and resources to detect issues, while systems with inadequate monitoring tools or ineffective team communication may struggle to detect issues altogether.
Measuring MTTD can be challenging, as issues and problems can vary in severity and complexity. However, by tracking MTTD over time, organizations can gain insights into their system’s performance and identify areas for improvement. Reducing MTTD is critical for ensuring timely issue resolution, improving system efficiency, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
III. Why Reduce MTTD?
Reducing Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) is crucial for improving system efficiency, reducing downtime, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Here are some reasons why reducing MTTD matters:
- Faster issue resolution: The longer it takes to detect an issue, the longer it will take to resolve it. By reducing MTTD, organizations can identify issues more quickly, allowing them to resolve them faster and reduce downtime.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Downtime and system issues can have a significant impact on customer satisfaction. By reducing MTTD and resolving issues quickly, organizations can minimize the impact on customers and improve overall satisfaction.
- Reduced costs: Downtime and system issues can also result in significant costs for organizations. By reducing MTTD, organizations can minimize the impact of issues on their operations and reduce associated costs.
- Enhanced system performance: Reducing MTTD can help organizations identify and address underlying issues that may be impacting system performance. By addressing these issues, organizations can improve the overall performance and efficiency of their systems.
- Compliance and regulatory requirements: Many industries and organizations have compliance and regulatory requirements that require them to detect and resolve issues quickly. By reducing MTTD, organizations can ensure they meet these requirements and avoid potential penalties or fines.
Overall, reducing MTTD is critical for improving system performance, minimizing downtime, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Organizations that prioritize MTTD can improve their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition.
IV. Strategies for Reducing MTTD
Reducing Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) requires a strategic approach and a combination of different tactics. Here are some effective strategies for reducing MTTD:
- Implement automated monitoring and alerting systems: Automated monitoring and alerting systems can help organizations detect issues quickly and alert relevant teams for prompt action. By setting up alerts for critical events and issues, organizations can reduce MTTD significantly.
- Improve communication and collaboration among teams: Effective communication and collaboration among different teams involved in software development and IT operations can help reduce MTTD. Encouraging regular meetings, sharing knowledge, and maintaining clear communication channels can help teams work together more effectively and reduce MTTD.
- Conduct regular assessments and reviews: Regular assessments and reviews of system performance and efficiency can help organizations identify areas for improvement and reduce MTTD. By reviewing metrics and logs, identifying patterns and trends, and addressing issues proactively, organizations can reduce MTTD and improve overall system performance.
- Leverage best practices and industry standards: Many best practices and industry standards exist for software development and IT operations. Adopting these practices and standards can help organizations improve their processes, reduce MTTD, and enhance system performance.
- Implement effective incident response processes: Effective incident response processes can help organizations detect and resolve issues quickly. By defining clear roles and responsibilities, establishing escalation procedures, and conducting regular drills and simulations, organizations can improve their incident response processes and reduce MTTD.
Incorporating these strategies can help organizations reduce MTTD and improve overall system performance and efficiency. However, it is essential to monitor and review the effectiveness of these strategies regularly and adjust them as necessary to ensure they are achieving the desired results.
V. Conclusion
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) is a critical metric that measures the average time it takes to identify an issue or problem in a system. Reducing MTTD is crucial for improving system performance, reducing downtime, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Strategies for reducing MTTD include implementing automated monitoring and alerting systems, improving communication and collaboration among teams, conducting regular assessments and reviews, leveraging best practices and industry standards, and implementing effective incident response processes.
By reducing MTTD, organizations can improve their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition. However, reducing MTTD requires a strategic and proactive approach, and it is essential to monitor and review the effectiveness of these strategies regularly. Overall, reducing MTTD is critical for ensuring timely issue resolution, improving system efficiency, and enhancing customer satisfaction.


